·The Composition and Working Principle of Battery
A battery is consist of the anode, the cathode, the electrolyte, the diaphragm and the container. It converts energy by oxidation - reduction reaction.
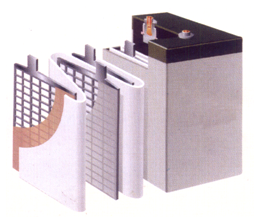
The active material at the anode of the battery are usually metal oxides: halogen and halide, oxygen or oxysalt, while the active material at the cathode are low potential metal or hydrogen.
The electrolyte is an aqueous solution of acid, alkali or salt. There are also solid electrolytes.
When the battery works, electrochemical oxidation reaction occurs and the active material at the cathode release electrons, which, in the function of the potential difference between two electric poles, transfer from the cathode to the anode through external circuit. And electrochemical reduction reaction occurs to the active material at the anode as they accept electrons. Meantime, the ions of the electrolyte transfer the current inside the battery through diffusion and electrical migration.
The chemical equation is as follows:
Cathode-------- Lead dioxide
Anode -------- Spongy lead
PbO2 +2 H2SO4 + Pb = PbSO4 +2 H2O + PbSO4
The diaphragm can seperate the anode and the cathode to prevent short circuit. It is usually made of porous rubber, plastic, cellulose membrane and so on.
The container of a battery is made of rubber, plastic, stainless steel and other corrosion-resistant materials.
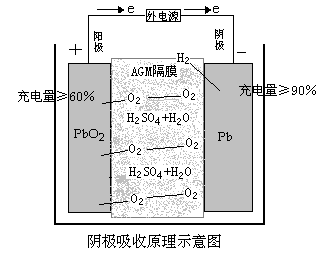
Battery Charging
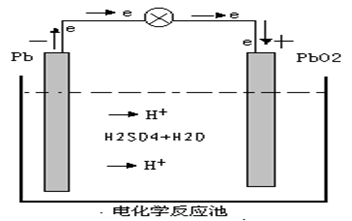
Battery Discharging







 Copyright © 2003 - 2023 . All Rights Reserved
Copyright © 2003 - 2023 . All Rights Reserved